Waste generation is a by-product of life. From machines and industries to plants and animals, everything under the sun generates waste in one form or another. At the end of the day, it is critical to dispose these waste products with utmost care and efficiency so as to prevent contamination of our world. Since waste comes from different sources and in different forms, it is divided into a large number of categories. One of the most important of these is biomedical waste, which, if not disposed properly, can result in a threat to living organisms.
In essence, biomedical waste is the liquid or solid waste and effluents generated in medical facilities, clinics and hospitals. This waste is generated as a consequence of treatment, diagnosis, immunization and sterilization of humans and animals. The containers and equipment used during medical procedures also fall under this category.
The management and disposal of biomedical waste is of a highly critical nature. This is because of the high likelihood of such waste to infect or poison anything that comes in contact with it. A medical facility such as a hospital produces used bandages and dressings, packaging, blood, used infusion kits, sharps such as used needles and syringes, human and animal tissue material, fluids, cultures, stocks, medicines, etc. on a regular basis.
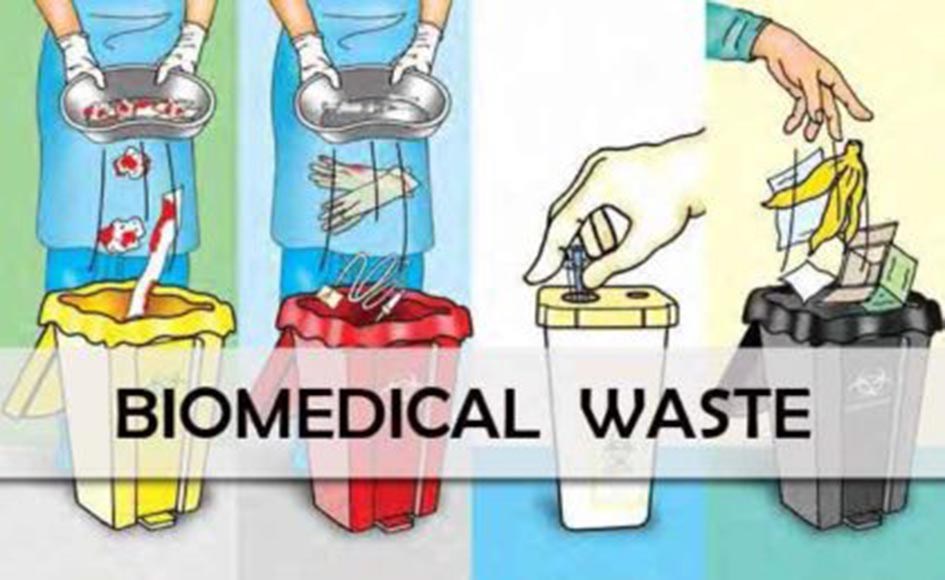
Broadly speaking, biomedical waste can be divided into:
- Pharmaceutical – Expired and non-usable substances, drugs and medicines
- Chemical – Reagents and chemicals used in medical setups
- Pathological – Body parts and fluids
- Infectious – Waste from lab cultures, isolation wards, etc.
- Sharps – Knives, scalpels, needles, syringes, etc.
- High metal content – Batteries, thermometers, and other equipment which utilize chemicals
- Genotoxic – Waste products that could be mutagenic, carcinogenic, or irritating
Due to the sensitive nature of this waste, it is not disposed in the open. Special methods, techniques and precautions need to be followed to properly manage and get rid of biomedical waste responsibly.
To accomplish this, a proper biomedical waste management process has to be followed.
Step 1: Collection & Segregation
When it comes to biomedical waste, one cannot simply throw it in common waste disposal or recycle bin. This is collected in containers that are sturdy, resilient, and do not break while handling. For this purpose, colour-coded containers, plastic bags and sharps disposal devices are used to segregate different categories of waste properly. Another critical element of this phase is non-hazardous cleaning of healthcare setups which requires proper kits including face masks, head caps, PVC aprons, sterile gloves, etc.
Nowadays, most of these biomedical waste disposal, cleaning and management equipment can be bought online in bulk from genuine medical supply portals such as Smart Medical Buyer. From the highest quality nitrile gloves in India to industry-renowned Becton Dickinson sharps collectors, all your medical establishment’s biomedical waste disposal waste management requirements can be taken care of at Smart Medical Buyer.
Step 2: Storage & Transportation
After segregation comes storage and transportation. It is important that the storage of such hazardous waste be done at a facility which is inaccessible to general public and is leakage and contamination-proof. Special refrigeration units and vehicles are also needed to store and transport biomedical waste in order to eliminate the risk of infection
Step 3: Treatment
Finally, biomedical waste requires appropriate treatment depending upon its category. While pathological and pharmaceutical waste is incinerated directly, other wastes such as sharps, containers, packaging, biological and chemical by-products are disposed via autoclaving, microwaving or enzyme destruction.
